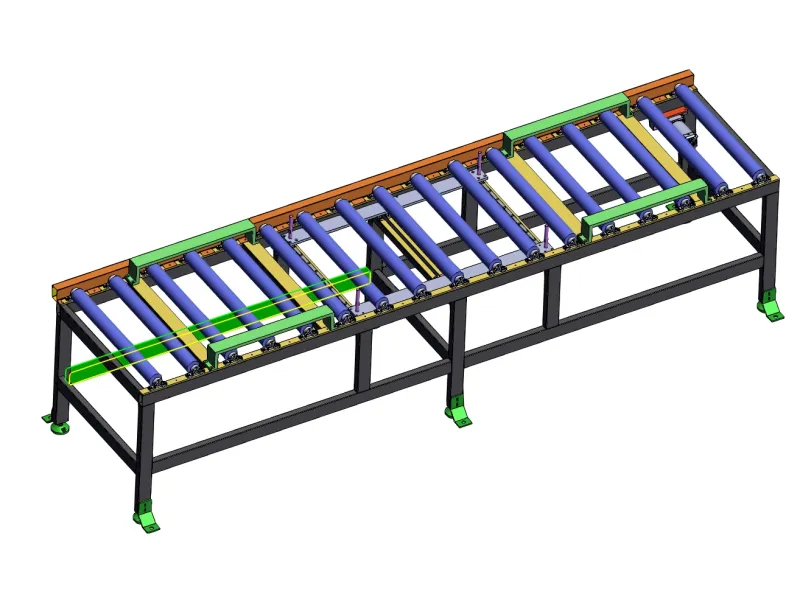

Powered Roller Conveyor Design
Designing a powered roller conveyor involves creating a system that uses motor-driven rollers to transport items with precise control, suitable for automated, high-volume, or heavy-duty applications. The design must ensure efficient material flow, load stability, and integration with your facility's layout and operational needs. Below is a detailed guide on the key design considerations and steps for creating an effective powered roller conveyor, covering both straight and curved configurations.
Key Design Considerations
1. Load Specifications
- Weight: Light-duty (up to 200 lbs), medium-duty (200–1,000 lbs), or heavy-duty (1,000 lbs+).
- Size: Length, width, height of items (e.g., 12" x 10" boxes, 48" x 40" pallets).
- Shape: Flat-bottomed, stable items (e.g., boxes, totes, pallets) work best; irregular items may need special rollers.
- Design Tip: Items must span at least three rollers for stability.
2. Conveyor Width
- Range: 12"–24" for light-duty; 24"–48" or more for heavy-duty.
- Calculation: Widest item + margin (e.g., 12" box + 4" = 16" width).
- Design Tip: Balance width for stability without wasting space or cost.
3. Conveyor Length
- Range: 5–100 feet, often modular (e.g., 5' or 10' sections).
- Design Tip: Match to transport distance; longer runs may need multiple drive motors.
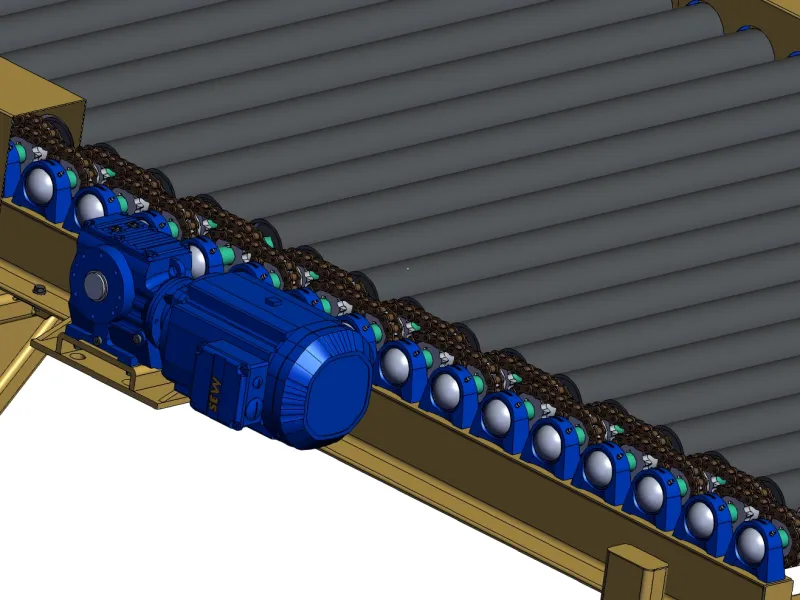
This is a roller conveyor using chain drive belt.
4. Roller Design
Diameter:
- 1.5"–1.9" for light-duty (easier to drive).
- 2.5"–3.5" for medium/heavy-duty (durable, high capacity).
Material:
- Steel: Durable, coated for rust resistance or grip.
- Plastic: Lightweight, for delicate/light loads.
- Aluminum: Balances strength and weight.
- Bearings: Precision bearings for smooth, frequent use; heavy-duty for high loads.
- Tapered (Curved Sections): Wider at outer edge, narrower inside for smooth turns.
5. Roller Spacing
- Rule: Minimum three rollers under the item (e.g., 12" item = 4" spacing or less).
- Range: 2"–6" centers; closer for small/light loads, wider for large/stable loads.
- Design Tip: Optimize spacing to reduce roller count while ensuring support.
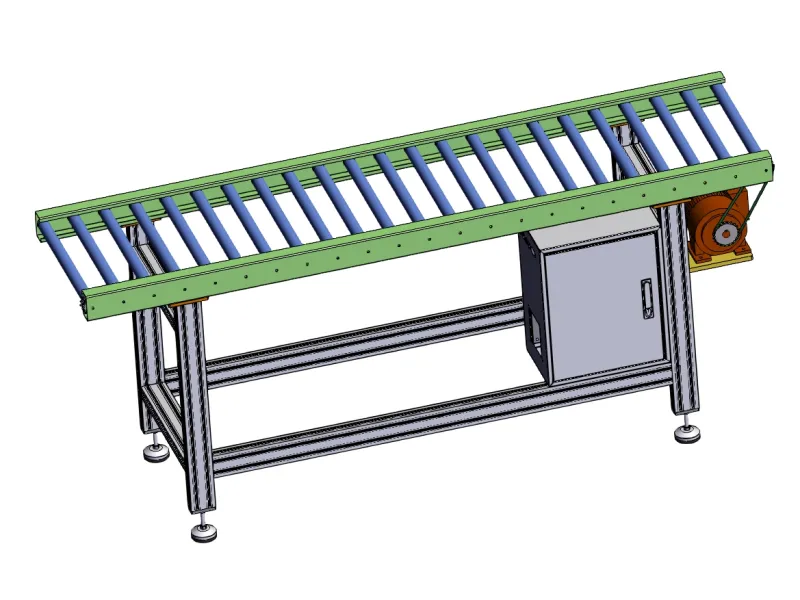
6. Drive Mechanism
Options:
- Motorized Rollers: Internal motors (e.g., 24V DC); quiet, precise, energy-efficient, zoned control.
- Chain-Driven: Chains link rollers; robust, for heavy loads or harsh conditions.
- Line Shaft: Shaft with bands drives rollers; cost-effective, light/medium loads.
- Belt-Driven: Belts under rollers; smooth, less common.
- Motor Power: 1/2 HP for light-duty; 1–5 HP for heavy-duty, based on load and speed.
- Design Tip: Motorized rollers suit automation; chain-driven excels for pallets.
7. Speed and Control
- Speed: 30–150 ft/min, adjustable for flexibility.
- Basic Control: On/off or fixed speed.
- Advanced: Sensors, PLCs, or variable frequency drives (VFDs) for zoned accumulation, automation.
- Design Tip: Match speed to throughput; sensors enable accumulation or flow control.
8. Frame Design
- Material: Steel for durability; aluminum for lighter setups; stainless steel for washdown.
- Structure: Two side rails with cross-bracing; curved for turns, straight for linear runs.
- Height: 12"–36" (low-profile for pallets, ergonomic for manual tasks).
- Design Tip: Reinforce for heavy loads; adjustable legs align with other systems.
9. Accumulation (Optional)
- Zero-Pressure (ZPA): Sensors stop rollers per zone; no contact, ideal for fragile loads.
- Low-Pressure: Rollers slip; slight contact, for sturdy loads.
- Design Tip: ZPA needs motorized rollers or sensors; low-pressure suits chain-driven.
10. Safety and Support Features
- Side Guides/Rails: Prevent items from derailing (e.g., 2"–6" high).
- Guards: Cover chains, motors, or pinch points.
- Emergency Stops: Accessible for quick shutdown.
- Supports: Legs or stands every 5–10 feet, based on load.
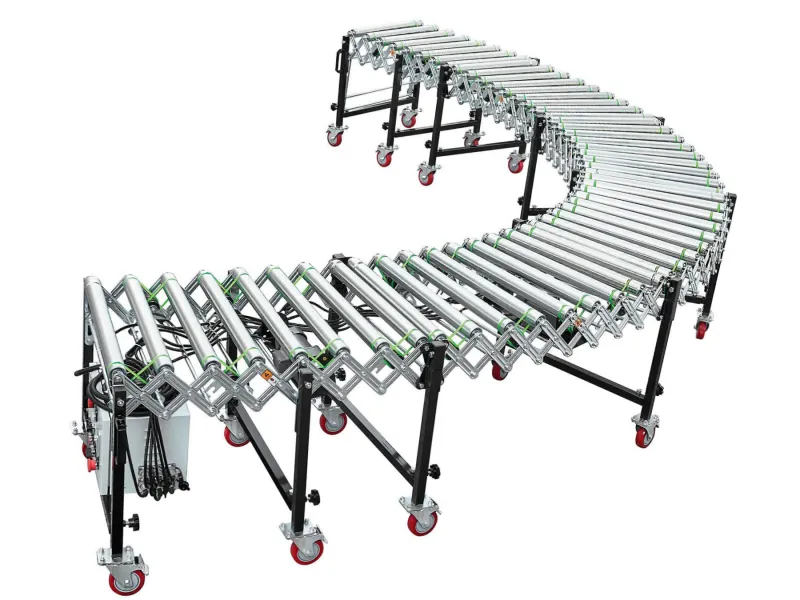

This is a flexible powered roller conveyor system.
Design Steps
1. Analyze Requirements
- Define load (e.g., 50-lb boxes, 18" x 12"), distance (e.g., 20 feet with 90° curve), purpose (e.g., transport to packing).
- Measure space (e.g., 25' x 10' area).
2. Calculate Dimensions
- Width: 24" (18" box + 6" margin).
- Length: 10' straight + 10' curved (90°, 24" inner radius).
- Outer Radius: 24" + 24" = 48".
- Arc Length: (π × 24 × 90) / 180 ≈ 37.7" (inner edge).
3. Select Roller Specifications
- Diameter: 1.9" for 50-lb boxes.
- Spacing: 4" centers (18" box spans 4–5 rollers).
- Straight: Steel, uniform 1.9".
- Curved: Tapered (1.9" inner to 2.5" outer).
4. Choose Drive System
- Motorized rollers (24V DC), 50 ft/min, zoned for accumulation.
- Motor: 1/2 HP, with PLC and sensors for ZPA.
5. Design Frame
- Steel, 24" wide, 30" height, supports every 5 feet.
- Curved section: 24" inner radius, reinforced cross-bracing.
6. Incorporate Features
- Side guides (3" high) for stability.
- Sensors per 5' zone for zero-pressure accumulation.
- Emergency stop and motor guards.
7. Validate Load Dynamics
- Test flow—ensure boxes stay aligned around curve, accumulate without pressure.
- Adjust speed or guides if tipping occurs.
8. Finalize and Prototype
- Create CAD drawing (e.g., 20' total, 10' straight + 90° curve, 24" wide).
- Simulate with supplier software or build a test section to confirm performance.
Example Design
- Scenario: A fulfillment center needs a powered roller conveyor to move 50-lb boxes (18" x 12") 30 feet with a 45° curve to a sorting station.
- Width: 24" (18" box + 6" margin).
- Length: 20' straight + 10' curved (45°, 30" inner radius).
- Rollers: 1.9" steel, 4" spacing; tapered in curve (1.9"–2.3").
- Drive: Motorized rollers (24V DC), 60 ft/min, 1/2 HP, ZPA with sensors.
- Frame: Steel, 30" height, supports at 0', 5', 10', 15', 20', 30'.
- Features: 3" side rails, emergency stop, accumulation zones (5' each).
- Capacity: 100 lbs/roller (300 lbs total support).
Design Tips
- Zoned Control: Plan zones (e.g., 3–5' long) for accumulation; match to item size.
- Tapered Rollers: Calculate taper for curves (outer/inner radius ratio).
- Power Efficiency: Use 24V DC rollers for lower energy costs.
- Supplier Tools: Leverage vendor CAD tools (e.g., Interroll, Hytrol) for accuracy.
A well-designed powered roller conveyor ensures precise, reliable material handling, tailored to your loads and automation needs. If you need help with calculations (e.g., motor sizing, zone length) or a specific design scenario, let me know!


Leave Me Your Requirement!