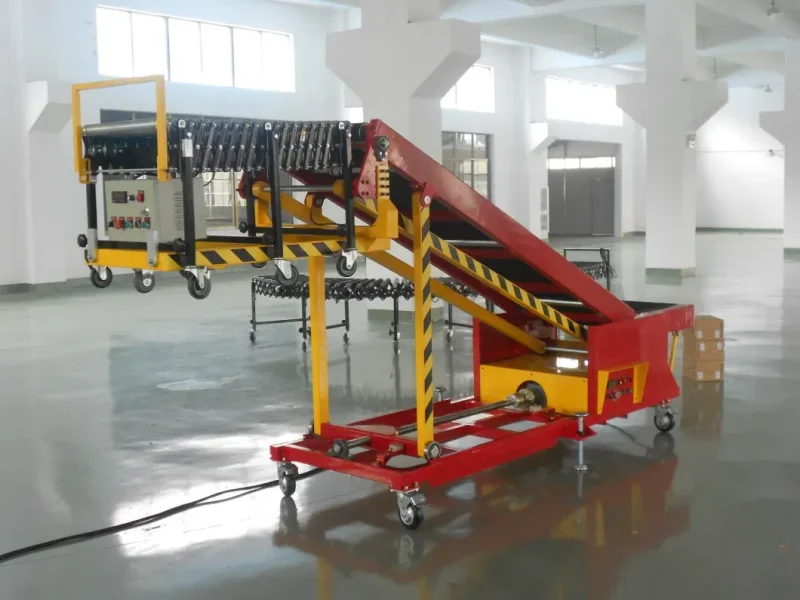

Container Loading and Unloading Conveyors
In today's fast-paced industrial environment, the efficiency of loading and unloading containers is crucial for maintaining smooth supply chain operations. Container loading and unloading conveyors are specialized systems designed to facilitate the swift movement of goods into and out of shipping containers, trailers, and trucks. These truck loading conveyors not only enhance productivity but also improve safety by reducing the need for manual handling. This comprehensive guide delves into the key features, types, benefits, and applications of container loading and unloading conveyors.
What Are Container Loading and Unloading Conveyors?
Container loading and unloading conveyors are mechanical systems engineered to transport goods directly into or out of shipping containers, trucks, or trailers. They are designed to handle various types of cargo, from loose parcels and packages to bulk materials. These conveyors can be fixed, mobile, telescopic, or flexible, catering to different operational requirements.
Key Features of Container Loading and Unloading Conveyors
1. Adjustable Length and Height
- Telescopic Sections: Many conveyors feature telescopic sections that can extend and retract, allowing them to reach deep into containers or trailers.
- Height Adjustment: Adjustable height settings accommodate different container sizes and loading dock levels, ensuring ergonomic operation.
2. Mobility
- Wheels and Casters: Some conveyors are equipped with wheels or casters, making them easy to move and position as needed.
- Portable Designs: Lightweight and compact designs facilitate quick deployment and storage.
3. Flexible Conveyance
- Flexible Conveyors: These conveyors can bend and twist to navigate around obstacles and fit into confined spaces.
- Roller and Belt Options: Depending on the material handled, conveyors may use rollers or belts to transport goods efficiently.
4. Safety Features
- Emergency Stop Buttons: Easily accessible emergency stops ensure quick response in case of hazards.
- Protective Guarding: Side guards and other protective measures prevent goods from falling off during transit.
5. Automation and Control
- Variable Speed Control: Operators can adjust the conveyor speed to match the workflow requirements.
- Automated Systems: Advanced models may integrate sensors and control systems for automated loading and unloading.
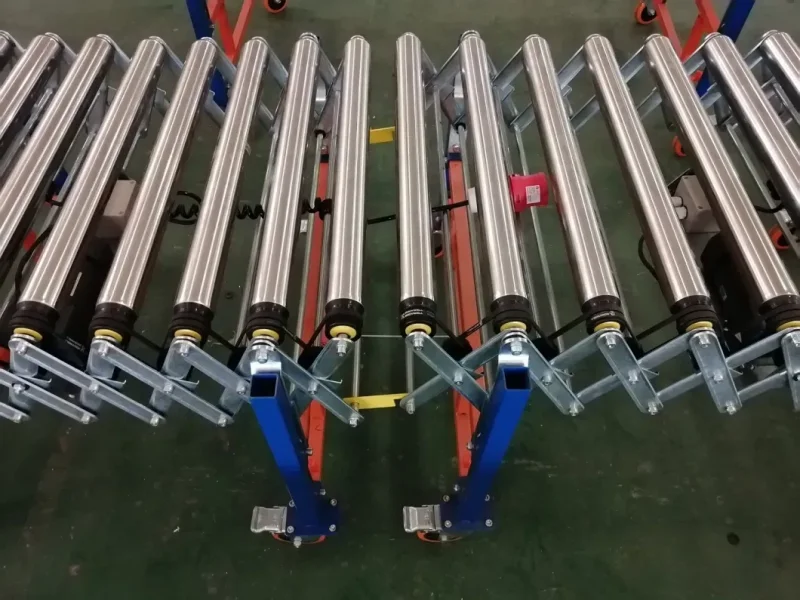
Types of Container Loading and Unloading Conveyors
1. Telescopic Belt Conveyors
- Description: These telescopic belt conveyors feature extendable sections that can reach deep into containers, providing a continuous and efficient loading and unloading process.
- Applications: Ideal for loading and unloading loose items such as parcels, boxes, and bags.
2. Flexible Roller Conveyors
- Description: Comprised of interconnected rollers, these flexible roller conveyors can flex and bend to accommodate various layouts and are often portable.
- Applications: Suitable for handling items with flat bottoms like boxes and cases.
3. Gravity Roller Conveyors
- Description: Utilizing gravity, these conveyors allow goods to move along rollers without the need for a motorized system.
- Applications: Best for operations where goods can be manually pushed or where slopes can be used.
4. Powered Roller Conveyors
- Description: Equipped with motorized rollers, these conveyors provide controlled movement of goods and are suitable for heavier items.
- Applications: Used in facilities handling heavy packages or requiring precise movement control.
5. Vertical Reciprocating Conveyors (VRCs)
- Description: Designed to move goods vertically, VRCs are used to transport items between different elevations, such as from ground level to a loading dock.
- Applications: Essential in multi-level facilities or where space constraints prevent the use of inclined conveyors.
Benefits of Using Container Loading and Unloading Conveyors
1. Enhanced Efficiency
- Reduced Loading Time: These conveyors significantly cut down the time required to load and unload containers, improving overall operational throughput.
- Continuous Flow: They facilitate a steady flow of goods, minimizing bottlenecks in the supply chain.
2. Improved Safety
- Reduced Manual Handling: By automating the movement of goods, these systems lessen the physical strain on workers and decrease the risk of injuries.
- Controlled Movement: Features like speed control and emergency stops enhance operational safety.
3. Cost Savings
- Labor Optimization: Automation reduces the need for manual labor, leading to long-term cost savings.
- Damage Reduction: Controlled handling minimizes the risk of product damage during transit.
4. Versatility
- Adaptability: With various types available, these conveyors can be tailored to specific industry needs and spatial constraints.
- Scalability: They can be expanded or reconfigured as operational demands evolve.
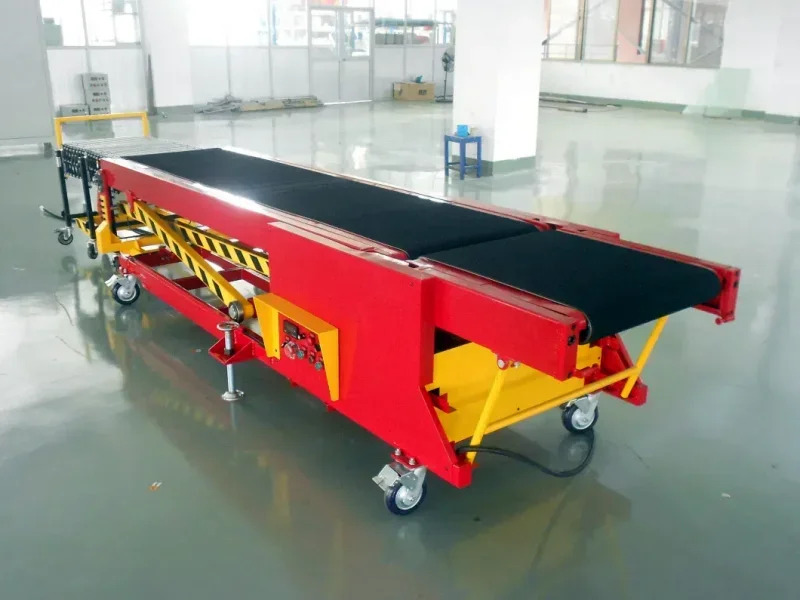

Applications of Container Loading and Unloading Conveyors
1. Logistics and Warehousing
- Parcel Handling: Efficient movement of packages in courier and postal services.
- Inventory Management: Streamlining the process of stocking and retrieving goods.
2. Manufacturing
- Component Supply: Feeding parts and materials into the production line.
- Finished Goods Dispatch: Loading completed products for shipment.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
- Bulk Material Handling: Transporting raw materials like grains or packaged goods.
- Cold Storage Facilities: Specialized conveyors designed to operate in temperature-controlled environments.
4. Retail Distribution
- Store Replenishment: Facilitating the distribution of merchandise to retail outlets.
- E-commerce Fulfillment: Managing the high volume of orders in online retail.
5. Agriculture
Produce Handling: Moving agricultural products such as fruits and vegetables into storage or transport vehicles.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Container Loading and Unloading Conveyor
1. Type of Goods
- Size and Weight: Ensure the conveyor can handle the dimensions and weight of the items.
- Material Nature: Consider whether goods are fragile, abrasive, or require special handling.
2. Operational Environment
- Space Constraints: Assess the available space to determine the appropriate conveyor size and type.
- Environmental Conditions: Factor in temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals.
3. Throughput Requirements
- Volume of Goods: Choose a conveyor system that can handle the expected volume efficiently.
- Speed Needs: Ensure the conveyor's speed capabilities align with operational demands.
4. Integration Capability
- Existing Systems: The conveyor should integrate seamlessly with current material handling equipment.
- Future Expansion: Consider potential scalability for future operational growth.
5. Budget
- Initial Investment: Balance the upfront cost with the expected return on investment through efficiency gains.
- Maintenance Costs: Factor in long-term maintenance and operational expenses.
Maintenance and Safety Tips
1. Regular Inspections
- Component Checks: Routinely inspect belts, rollers, motors, and control systems for wear and tear.
- Alignment Verification: Ensure the conveyor is properly aligned to prevent operational issues.
2. Cleaning Protocols
- Debris Removal: Keep the conveyor free from debris that could cause jams or damage.
- Sanitization: In industries like food and pharmaceuticals, maintain strict cleaning standards.
3. Staff Training
- Operational Training: Ensure all operators are trained on the proper use of the conveyor system.
- Safety Procedures: Educate staff on safety protocols, including emergency stops and hazard identification.
4. Preventive Maintenance
- Scheduled Servicing: Implement a maintenance schedule to replace worn parts and lubricate moving components.
- Software Updates: For automated systems, keep software and control systems updated.
Container loading and unloading conveyors are indispensable tools in modern material handling, offering significant advantages in efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the various types available and considering the specific needs of your operation, you can select a conveyor system that not only meets your current demands but also adapts to future growth. Regular maintenance and adherence to safety protocols will ensure the longevity and reliable performance of these vital systems.


Leave Me Your Requirement!